Helium is one of the most unique and valuable elements on Earth. While many people associate helium with party balloons, this versatile gas has a wide range of uses in different fields, from medicine and science to entertainment and technology. As an inert, non-toxic, and lighter-than-air gas, helium plays an essential role in our everyday lives. This article explores the many ways helium is used and how it continues to contribute to modern advancements.

Table of Contents
- Introduction: What is Helium?
- 1. Helium in Balloons
- 2. Helium in Medicine
- 3. Helium in Scientific Research
- 4. Helium in Technology and Industry
- 5. Helium in Space Exploration
- 6. Helium in Entertainment
- Summary Table: Key Takeaways
Introduction: What is Helium?
Helium is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, and extremely light gas. It is the second most abundant element in the universe and is often found in natural gas fields. Despite its abundance in the cosmos, helium is relatively rare on Earth. Its unique properties, including its low boiling point and lack of reactivity, make it highly useful in various industrial and scientific applications.
Helium is typically produced through the extraction of natural gas or by liquefying air, which separates helium from nitrogen and other gases. Because of its non-toxic and non-flammable nature, helium is used in a wide array of applications that require safe, inert environments.
1. Helium in Balloons

One of the most common and popular uses of helium is in balloons. Thanks to helium’s lower density compared to air, it provides lift, causing balloons to float. This characteristic makes helium an ideal choice for party decorations, promotional events, and celebrations.
Why Helium in Balloons?
- Safety: Unlike hydrogen, helium is non-flammable, making it much safer for use in balloons.
- Lift: Helium is lighter than air, allowing balloons filled with helium to float.
- Longevity: Helium balloons can float for several hours to days, depending on the quality of the balloon and environmental conditions.
While helium balloons are mostly used for fun and entertainment, they also have applications in scientific research (such as atmospheric studies) and in industries that require controlled environments for testing equipment.
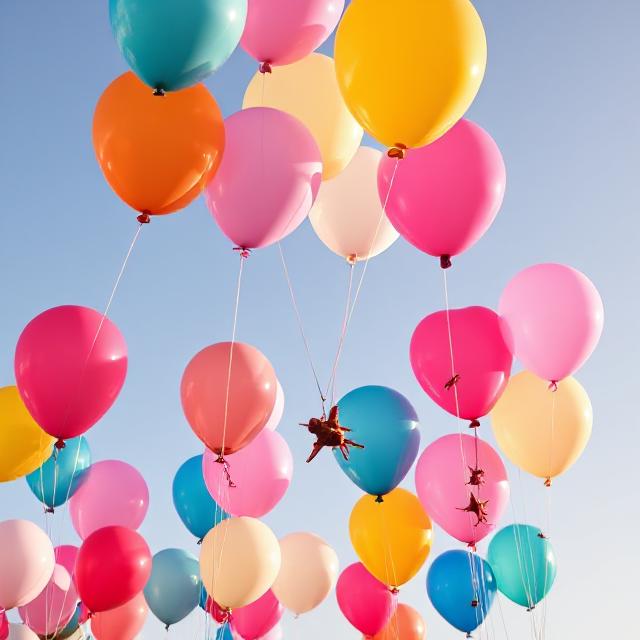
2. Helium in Medicine

Helium is crucial in the medical field, particularly in medical imaging and respiratory treatments. Its properties, such as its low boiling point and its ability to dilute oxygen, make it a valuable resource in various medical procedures.
Key Medical Uses of Helium:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Helium is used to cool the superconducting magnets in MRI machines, enabling them to function effectively.
- Respiratory Therapy: Helium is mixed with oxygen to create a helium-oxygen mixture (heliox), which helps improve breathing in patients with respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Neonatal Care: Helium is used to treat premature babies with underdeveloped lungs by helping to deliver oxygen more effectively.
The medical community relies on helium for various treatments and procedures, and its role in imaging technologies continues to be a significant factor in modern healthcare.
3. Helium in Scientific Research
Helium plays an essential role in scientific research, especially in the fields of cryogenics and particle physics. Due to its extremely low boiling point, helium is used to cool substances to near absolute zero, which is essential for numerous scientific experiments.
Scientific Applications of Helium:
- Cryogenics: Helium is used to cool superconducting magnets and other equipment that need to operate at very low temperatures, such as those used in particle accelerators like the Large Hadron Collider.
- Quantum Computing: Helium is also essential for maintaining the ultra-low temperatures required for quantum computers to function, as they rely on superconductivity.
- Laboratory Research: Helium is used in laboratories for various cooling applications, including experiments that require controlled low-temperature environments.
Without helium, many of the advancements in physics, computing, and other scientific fields would not be possible. Its unique properties make it invaluable for cutting-edge research.
4. Helium in Technology and Industry
Helium is used in various technological and industrial applications due to its non-reactive nature. It is employed in processes that require inert gases, such as in arc welding, leak detection, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Helium’s Industrial Uses:
- Arc Welding: Helium is used in welding processes, particularly in industries where high-quality, precision welding is required. It provides an inert atmosphere that prevents oxidation during welding.
- Leak Detection: Helium is used as a tracer gas to detect leaks in vacuum systems and high-pressure systems.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: In semiconductor production, helium is used to cool equipment and maintain an inert atmosphere.
Helium is essential for ensuring the quality, safety, and efficiency of industrial processes, and its role in manufacturing and production continues to expand as technology advances.
5. Helium in Space Exploration
Helium plays a critical role in space exploration. Its low boiling point and inert properties make it ideal for use in spacecraft and satellites. It is used in various systems, such as cooling systems for propulsion units and spacecraft fuel tanks.
Space Exploration Uses of Helium:
- Rocket Propulsion: Helium is used in rocket engines to pressurize fuel tanks and maintain a stable flow of fuel.
- Cooling Systems: Helium is used in cryogenic cooling systems to keep various spacecraft components at the required low temperatures.
- Satellites: Helium is used in satellites to control temperature and pressure, ensuring proper operation in the extreme environment of space.
Helium’s unique properties make it indispensable for ensuring the success of space missions, as it helps regulate temperature and pressure in spacecraft and rockets.
6. Helium in Entertainment
Helium is perhaps best known for its use in party balloons, but it also plays a role in entertainment beyond that. It is used in scientific demonstrations, magic shows, and even in creating special effects.
Entertainment Uses of Helium:
- Voice Changing: Inhaling helium temporarily alters the sound of the voice, causing it to become high-pitched. This effect is commonly used for comedic or novelty purposes.
- Party Decorations: Helium-filled balloons are essential for creating festive atmospheres during celebrations, adding to the fun and excitement of events.
- Special Effects: Helium is sometimes used in special effects for its properties, such as creating fog or lifting objects in a controlled manner during performances.
While helium’s use in entertainment is often lighthearted, it also contributes to the creative side of events and performances.
Summary Table: Key Takeaways
| Use | Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Balloons | Party and event decorations | Provides lift and safety |
| Medicine | Medical imaging, respiratory therapy | Helps in diagnostics and treatment |
| Scientific Research | Cryogenics, quantum computing | Enables low-temperature experiments |
| Technology | Arc welding, leak detection | Improves industrial processes |
| Space Exploration | Rocket propulsion, satellite temperature control | Supports space missions |
| Entertainment | Voice changing, party effects | Enhances fun and creativity |